Table of Contents
- What Is Technical SEO?
- Why Is Technical SEO Important?
- A 6-Step Checklist To Technical SEO Audit
- Step 1 – Audit Site Crawlability
- Step 2 – Audit Site Indexability
- Step 3 – Review Your Website Sitemap
- Step 4 – Audit Website Mobile-Friendliness
- Step 5 – Audit Website Page Speed
- Step 6 – Audit For Duplicate Content
- Wrapping Up
I’m quite certain that I don’t need to introduce the term SEO. We all know it’s the method of reaching the right audience by securing a higher position on the SERPs. When discussing SEO, our focus mainly revolves around on-page and off-page optimization. However, technical SEO is another important pillar that tends to get overlooked too often.
If I were to define technical SEO in one sentence, I would say it’s the process of optimizing your website to enhance its efficiency, allowing search engines to easily find, crawl, and index your content.
Auditing your website for technical SEO and implementing necessary changes can significantly enhance your organic reach. But first, let’s understand what is technical SEO a bit more thoroughly.
What Is Technical SEO?
While on-page and off-page SEO deals with the quality of content and external factors like backlinks, technical SEO deals with technical aspects of the website and user experience. It is all about optimizing the technical aspects of your website to make it more accessible for search engines to find, categorize, and index your content.
The goal is to eliminate any friction points between search engines and your website that could prevent search engine bots from crawling and discovering your content.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
While often overlooked, technical SEO can make or break your website’s organic growth.
Even if you have high-quality content with on-page best practices and a strong off-page game, it won’t appear on SERPs if search engines can not access your website. Additionally, search engines are also placing increasing emphasis on user experience, such as page load speed and mobile friendliness.
By improving the technical aspects of your website, you help search engines find and index your content more efficiently, thereby helping you achieve a better position on the SERPs.
A 6-Step Checklist To Technical SEO Audit
Technical SEO audits are not always easy to perform, especially if you have a large website with 100s of pages or those in multiple languages. Whether you run a small website with a few pages or manage a more complex website with hundreds of pages, these 6-Step technical SEO audit checklists will help you identify and fix technical issues on your website.
- Audit Site Crawlability
- Audit Site Indexability
- Review Site Sitemap
- Audit Mobile-Friendliness
- Audit Site Page Speed
- Audit for Duplicate Content
Step 1 – Audit Site Crawlability
Google and other search engines use bots to regularly crawl your website for new content and add it to their database. No matter how great an article is, if search engines can not crawl it, they will never show it to your intended audiences when they search for it online. As an SEO professional, it is our job to make this process easier for search engine bots to be able to crawl our website.
The most effective way to check your website for crawl issues are by examining your robots.txt file and using Google Search Console.
Audit Crawl Issues Using robots.txt
Robots.txt is a file that contains a set of instructions for search engine bots that tell them which URLs they can access. This file is often included in the source file of the website and can be accessed by adding /robots.txt to the end of any root domain.
This file specifies which parts of the website can be crawled or indexed by different search engine bots (e.g., Googlebot, Bingbot) and can include directions such as “Disallow” to block certain paths or “Allow” to permit access to specific resources.
Here is an example of robots.txt file on my website rabinmistri.com
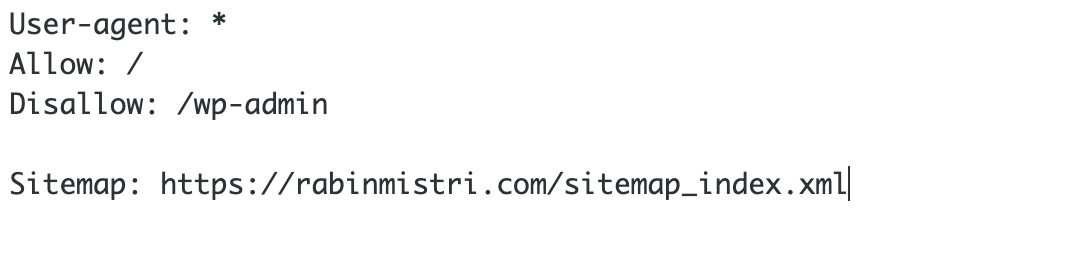
As we can see here, robots.txt file on my website is instructing all the search engine crawlers not to crawl any URLs that start with /wp-admin (my website backend).
By instructing not to crawl any specific URLs or URL path, you can save on server resources, bandwidth, and your crawl budget.
It is also very common to make mistakes and accidentally set disallow rules for pages that you actually want search engines to crawl and index. Since robots.txt is the first file that bots see when they are crawling your site, they may not crawl certain pages due to misconfiguration.
Cloudflare has a great article on robots.txt. You can follow it to create a robots.txt file based on your SEO requirements. Alternatively, you can use any online robots.txt file generator, such as the one from SEOptimer.
Step 2 – Audit Site Indexability
Now that we have audited whether search engine bots can actually crawl our website, we need to next shift our focus to whether those pages are being indexed by search engines.
In simple terms, Indexing is when a search engine organizes and stores your content after crawling your page. Later, this content is displayed on the search page when someone searches for relevant keywords.
For many reasons, search engines may not index your page even after crawling it. As an SEO professional, it is our job to identify those issues and take appropriate action to resolve them.
To conduct a thorough audit of your site for indexability issues, we will need the following tools:
- Screaming Frog (Free)
- Google Search Console
- Google.com
1. Manual Search on Google
One of the easiest ways to check how many pages from your website have been indexed by Google is by doing a manual search on Google.com
Go to Google.com and use the search operator “site:yourdomain.com”. This will display all the pages indexed by Google.
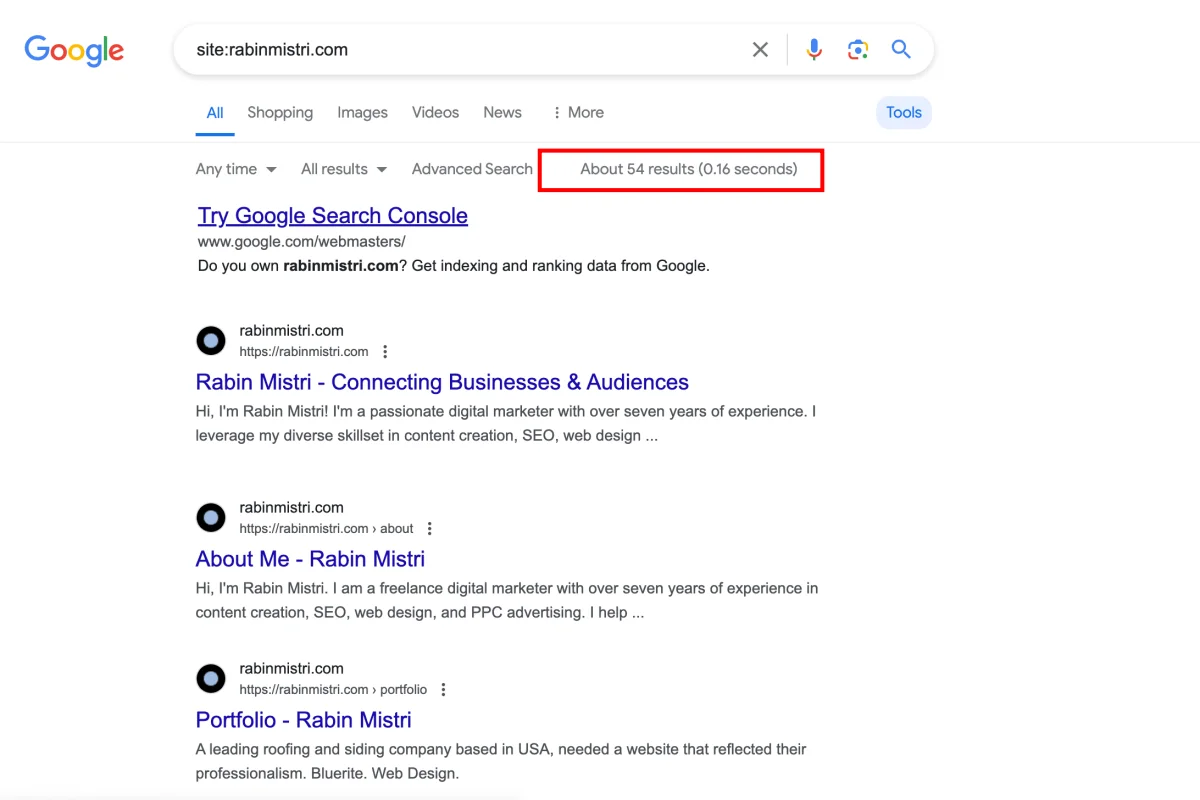
Here in this example, we see that about 54 URLs from my website have been indexed by Google so far. (If you do not see this number, try searching from a desktop browser and click on the ‘Tools’ button)
If you notice a big difference between the number of pages indexed by Google and the actual number of pages on your website, you may want to start investigating this further.
What to Look for in These Search Results?
- Ensure that the HTTPS version of your site is indexed by Google.
- Check for any duplicate pages in the Google index list.
- Verify that any rich snippets installed are displayed correctly.
- Review whether any pages that shouldn’t be indexed by Google are present on Google.
- Compare the total number of pages on your website to those indexed by Google.
Follow similar steps for other search engines like Bing and Yahoo.
2. Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog SEO spider is my primary website crawler tool that I use often for several reasons, including technical SEO audits. It is a website crawler application that allows you to crawl up to 500 URLs for free (with the option for unlimited URLs if you purchase a license). It is a powerful little tool that comes with several features that make your SEO audit process much faster.
How to Audit Website Indexability Using Screaming Frog?
Download the SEO Spider Tool from their website and install it on your computer.
Now, open the program, type in the domain name in the URL search bar, and click ‘start’.
Soon, the program will begin crawling your website, and list all the URLs on your website in a table format along with other SEO information and issues.
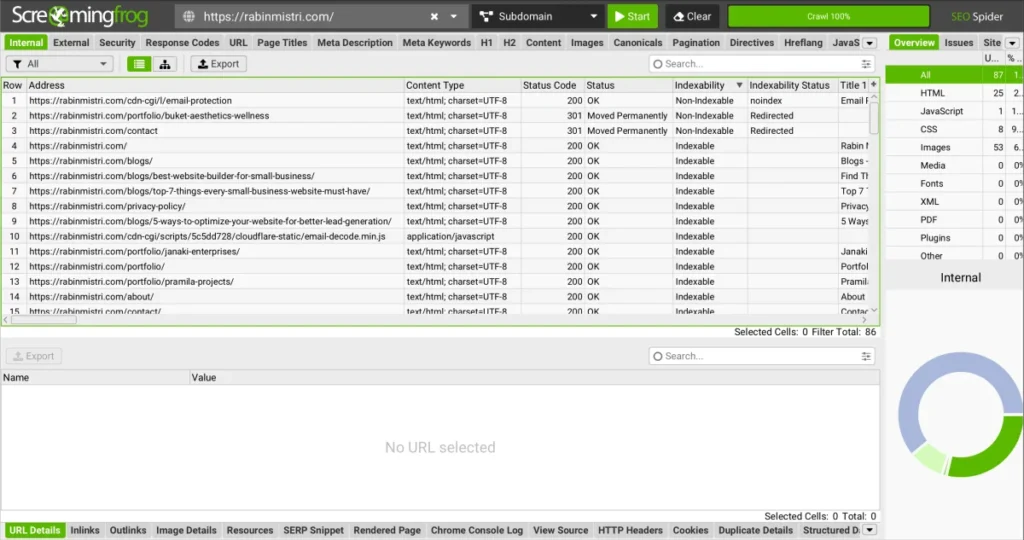
For now, we are only focusing on two specific columns:
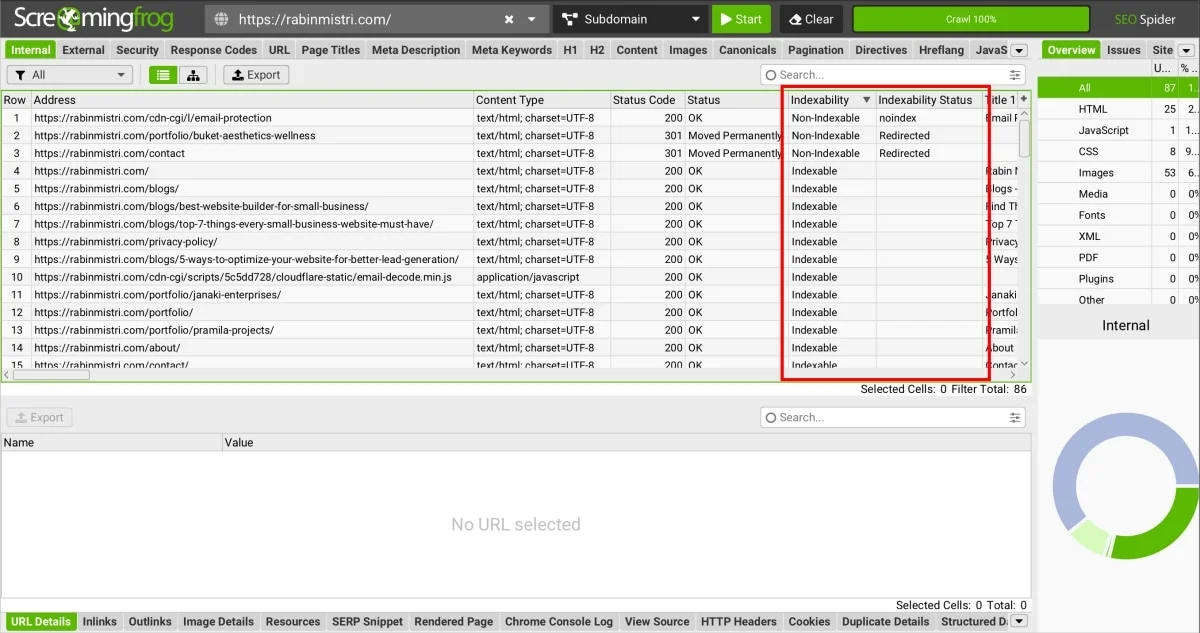
- Indexability: This column indicates whether a page/URL is indexable or not
- Indexability Status: If a page is not indexable, then this column will display the reason. For example, in the above screenshot, you will notice, that two URLs are non-indexable due to redirection, while one URL has a ‘noindex’ tag.
This SEO tool is a lifesaver for most SEO professionals. It lets you easily check your website for common SEO issues all in one place. You can quickly audit data such as meta title, meta description, broken links, and indexability in bulk.
Semrush’s Site Audit and Ahrefs’ Site Audit are two excellent alternatives to Screaming Frog.
3. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool with tons of data and reports from Google on how your website is performing on the Google search. You can use this data and information to improve the performance of your website on Google search pages.
We will use its coverage report to audit website indexability issues.
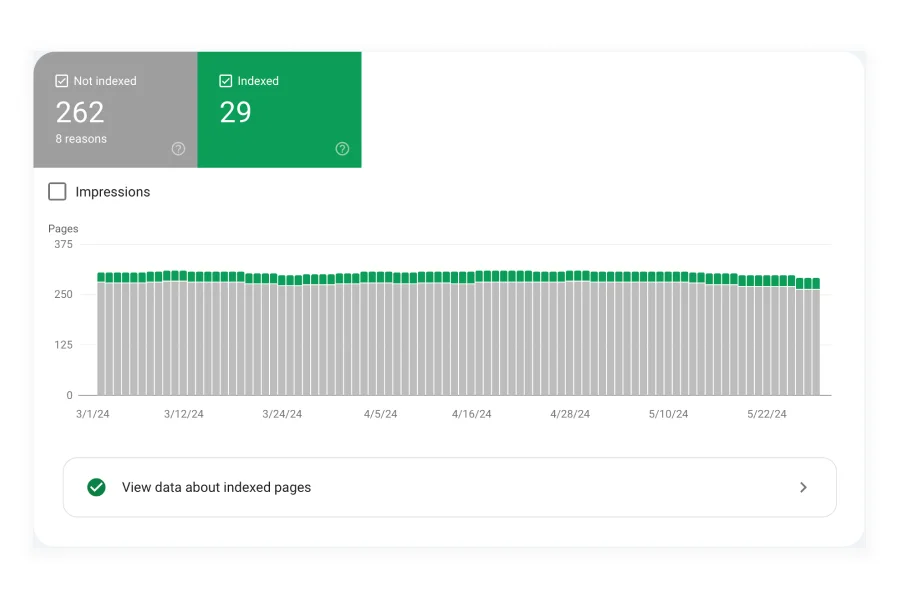
This report lists all the pages discovered by Google. It includes the pages currently indexed, pages with indexing errors, and pages that are excluded along with the reasons for their exclusion.
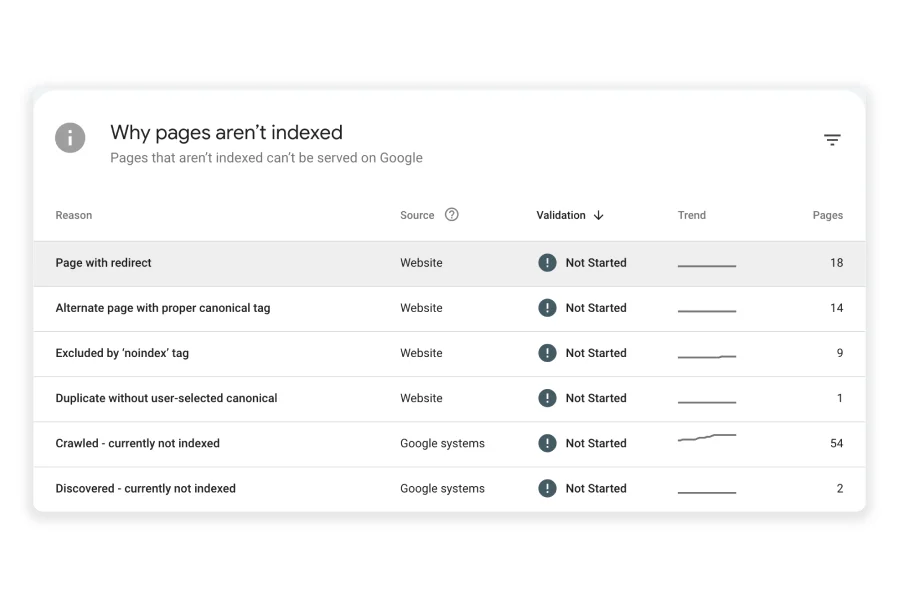
The screenshot above is from the GSC coverage report of one of my client’s websites. Here you can see, that there are 9 pages excluded due to the ‘noindex’ tag.
Additionally, 54 pages were crawled by Google bot but not indexed, while 2 pages have been discovered by Google but not yet indexed.
You can click on each of these reasons to see the affected URLs and the reasons behind the issues, which will help you fix them.
These three methods enable you to effectively visualize how search engines are indexing your website pages and identify any discrepancies.
Step 3 – Review Your Website Sitemap
An XML sitemap is like a map of your entire website for search engine bots. Search Engines use sitemaps to discover and understand different pages on your website, and ideally rank them on the SERPs.

The importance of sitemaps makes it crucial that your sitemap is well-structured and follows SEO best practices:
- Properly format your sitemap in an XML document.
- Include all the pages you want Google and other search engines to find and index.
- Exclude all the pages that you do not want search engines to crawl.
- Exclude any URLs with a ‘noindex’ tag.
- Keep your XML sitemap updated with new URLs as they go live.
- Only include a canonical version of any given URL.
If you are using WordPress, you can install a popular SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or All In One SEO to automatically generate an XML sitemap for your website.
Alternatively, you can create an XML manually or use any online XML generator.
Once you have an updated and well-structured sitemap, you should resubmit your sitemap to Google Search Console.
Step 4 – Audit Website Mobile-Friendliness
The rise of smartphones has caused a significant shift in the way people access the internet. Currently, over 60% of web traffic originates from mobile devices. If your website is not optimized for mobile use, you could potentially be missing out on 60% of your potential traffic.
For the past few years, Google has increasingly prioritized mobile devices and has transitioned to mobile-first indexing. Essentially, this means that Google now primarily indexes the mobile version of websites as opposed to the desktop version.
If your website is not well-optimized for mobile devices, Google will not index your page, and it will never show it on the SERP.
To assess how well or poorly your website is performing in terms of mobile-friendliness, Google Search Console includes a handy “mobile usability” report.
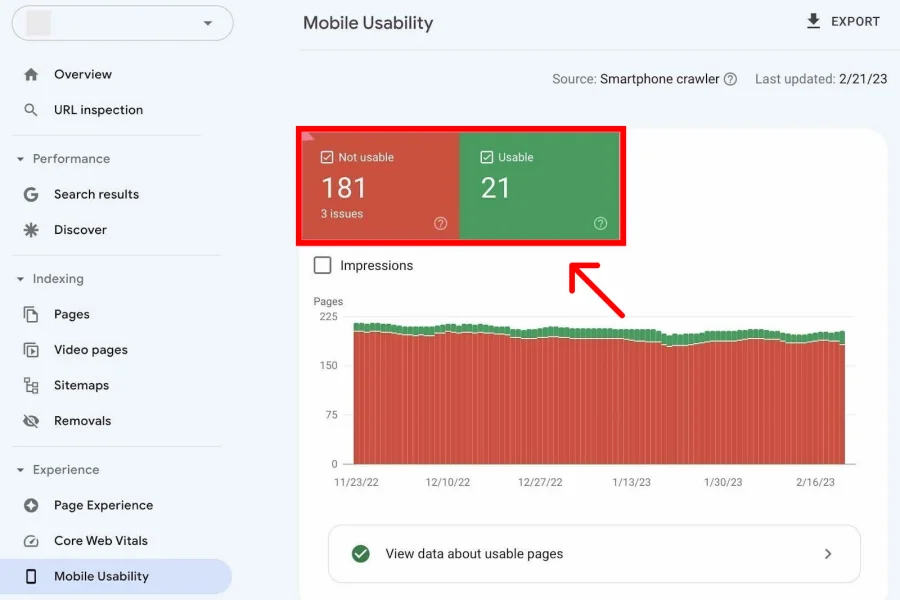
This report is straightforward and divided into two categories – ”Useable” and “Not Useable”
As you scroll down, you will find a section that lists all issues detected by Google that make your pages not useable for mobile. Clicking on any specific issue will allow you to see all the affected pages and provide links to fix the issue.
It is also a good practice to manually check each page for any user experience issues.
Additionally, you can use online mobile-friendly test tools such as Bing Mobile Friendliness Test Tool.
Step 5 – Audit Website Page Speed
Website page speed refers to the time it takes for your website to load once someone clicks or types your website address. Even if you have the best content, users will leave without consuming it if it takes too long to load.
“The probability of bounce increases 32% as page load time goes from 1 second to 3 seconds.” – Google/SOASTA Research, 2017.
Slow page speed not only creates a bad experience for the users but also impacts your ranking on search engines. Google has been considering website page speed as a ranking factor since 2018.
We will be using Google’s PageSpeed insight tool to perform an effective page speed audit.
Audit For Website Page Speed Using Google PageSpeed Insight
Google PageSpeed Insight is a free tool from Google designed to help optimize website performance for both mobile and desktop users.
It gives a score between 0 and 100 based on your website’s performance and efficiency. The higher the score, the better the website is in terms of speed and performance.
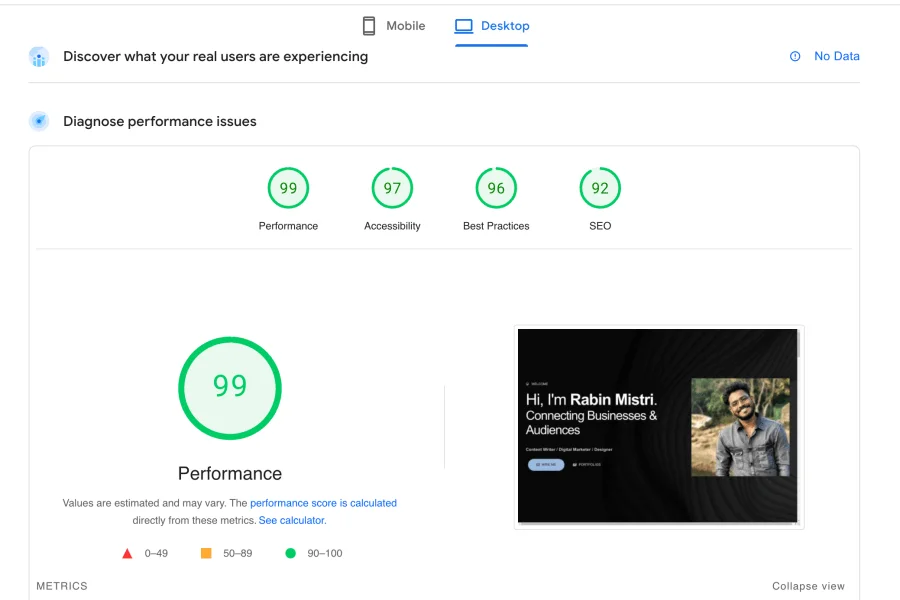
There are a few metrics that influence how Google assigns a score to your website. The three most important are called core web vitals, and they are:
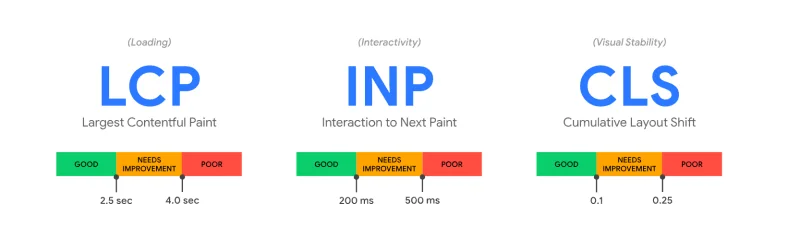
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): It measures how fast the largest visible element on your page loads.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): This measures how long the website takes to become responsive after a user interacts with the page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures how much the elements on a page move around unexpectedly while it loads.
Understanding core web vitals is vital for improving your score on Google PageSpeed Insight.
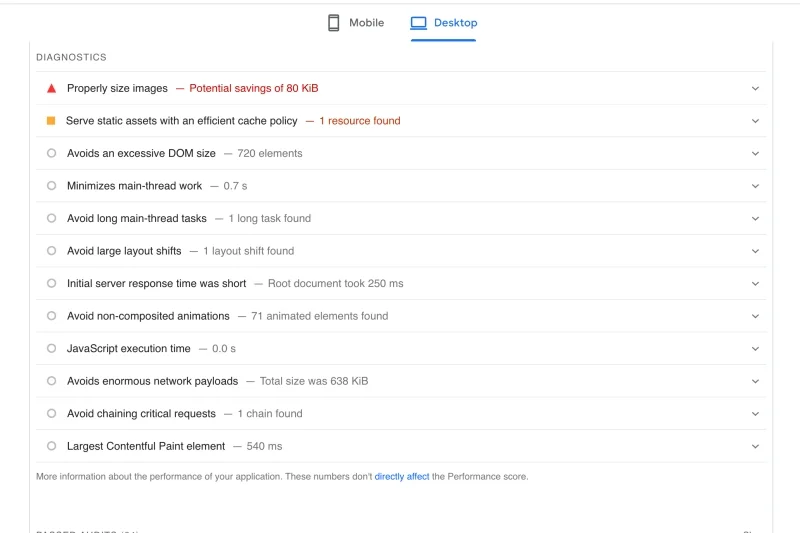
Additionally, PageSpeed Insight provides recommendations for improving your site performance. These suggestions are based on the diagnosis of your website.
GTmetrix is another excellent website performance analysis tool that I love and highly recommend.
Step 6 – Audit For Duplicate Content
The last step in a technical SEO audit involves addressing duplicate content issues.
In SEO, duplicate content is strongly discouraged. While there is no specific penalty for having duplicate content, Google prefers not to rank websites or pages with duplicated content.
In SEO, duplicate content refers to content that is identical or very similar to content found on other pages of the same website.
Even though there is no harsh penalty for duplicate content, it can still hurt your ranking. This is because Google may have difficulty determining which page to display on the SERPs, making it easier for your competitors to gain better visibility.
Primarily, duplicate content issues may arise in two main ways:
- Duplicate content due to technical misconfiguration
- Duplicate content due to content similarities
1. Technical Misconfiguration: Spot and Fix The Issue
Technical misconfigurations are often overlooked, resulting in search engines indexing multiple versions of the same content. Two common misconfigurations that can lead to duplicate content issues are:
1. URL Variations
One common reason for duplicate content on a site is having multiple versions of the URLs. For example, most websites today have HTTPS protocol. But the same website can also be accessed using HTTP protocol.
Google and other search engines consider both versions different leading to duplicate content issues.
Similarly, WWW and non-WWW can cause duplicate content issues.
The simplest solution is to create a sitewide 301 redirect rule to direct traffic to the preferred version of your website.
2. URL Parameters
URL parameters are additional elements added to a URL to help users filter or sort content or to help a website implement tracking. These parameters are always accompanied by a question mark.
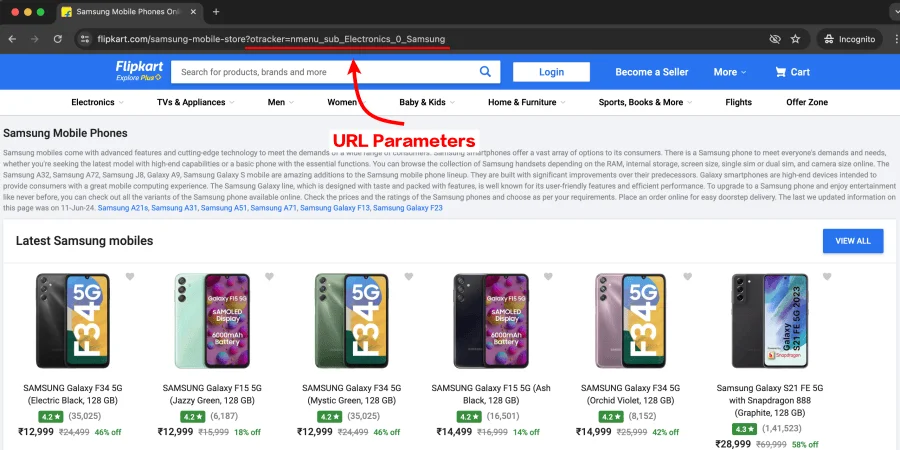
Even though the visuals may slightly differ, the content mostly remains the same. Google usually groups these URLs and indexes only one version of the URL. However, in some cases, Google may index multiple versions of the URL, which may harm your overall SEO performance.
If you use URL parameters for tracking or other reasons, Google recommends that you take the following actions:
- Remove unnecessary URL parameters to keep the URL as clean as possible.
- Use canonical tags to direct bots to the original URL with no parameters.
2. Content Similarities: Spot and Fix The Issue
Apart from technical reasons, your website may also face duplicate content issues if you have similar content (word-for-word or slightly rewritten) on different pages on the same website.
In simple words, having pages without unique information can be seen as duplicate content and can negatively impact your search engine rankings.
How to Find Similar Content?
Finding similar content that has already been published on your website can be challenging and time-consuming. Personally, I use the following two methods to find similar content:
1. Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is making another appearance in this article. It is a powerpack tool for SEO professionals and has lots of cool functions. You can configure Screaming Frog to identify duplicate content on the website.
With Screaming Frog, you can detect both ‘exact duplicates’ content as well as ‘near duplicates.’
- Exact Duplicate: As the name says, exact duplicate refers to content on 2 or more pages to have exact word-to-word content.
- Near Duplicate: It refers to 2 or more pages on the website that may not have exact duplicate content, but have sufficient similar texts to relate them to each other.
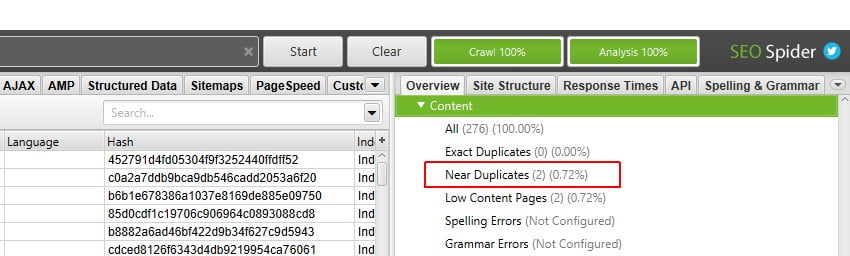
By default, Screaming Frog can identify exact duplicate pages. However, to identify near duplicate content, we need to configure the program to find near duplicates with a 70% to 90% similarity match.
Screaming Frog has this detailed guide on how to configure your program to find near duplicate content with all the necessary settings.
2. Siteliner.com
Siteliner is an online website crawler with a focus on finding duplicate content.
To use it, simply visit the website and enter your website URL.
Siteliner will then crawl your website and generate a site report. Once the report is generated, click on the “Duplicate Content” option from the main menu to access the duplicate content report.
In this report, you will find a table listing all the pages on your website that have duplicate content.
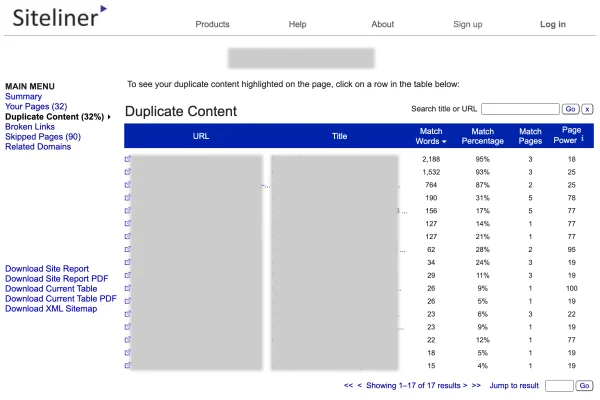
The table also provides important information such as the percentage of matched content, the number of pages with similar content, and the number of matched words.
Wrapping Up
To wrap up, a thorough technical SEO audit should be part of your SEO strategy and can have a significant effect on your website’s performance on SERPs.
A technical SEO audit ensures that your website is technically sound and not missing out on potential opportunities. It won’t matter how great your on-page and off-page SEO is if your site is not well-optimized for search engine bots to find and crawl.
This article is by no means a complete guide, as technical SEO can get more complex the deeper you dive into it. However, this 6-step technical SEO checklist is a good starting point for any SEO professional to ensure their website is well-optimized for search engine bots.
Regular technical SEO audits can help a business stay on top of any technical issues and maintain its online growth and performance.
As always, if you have any questions regarding technical SEO audits, feel free to reach out to me on LinkedIn or Instagram.




2 Responses
Great article on performing a technical SEO audit! The steps are easy to follow and very practical. Thanks for sharing this valuable information.
Thank you so much Kai 🙏